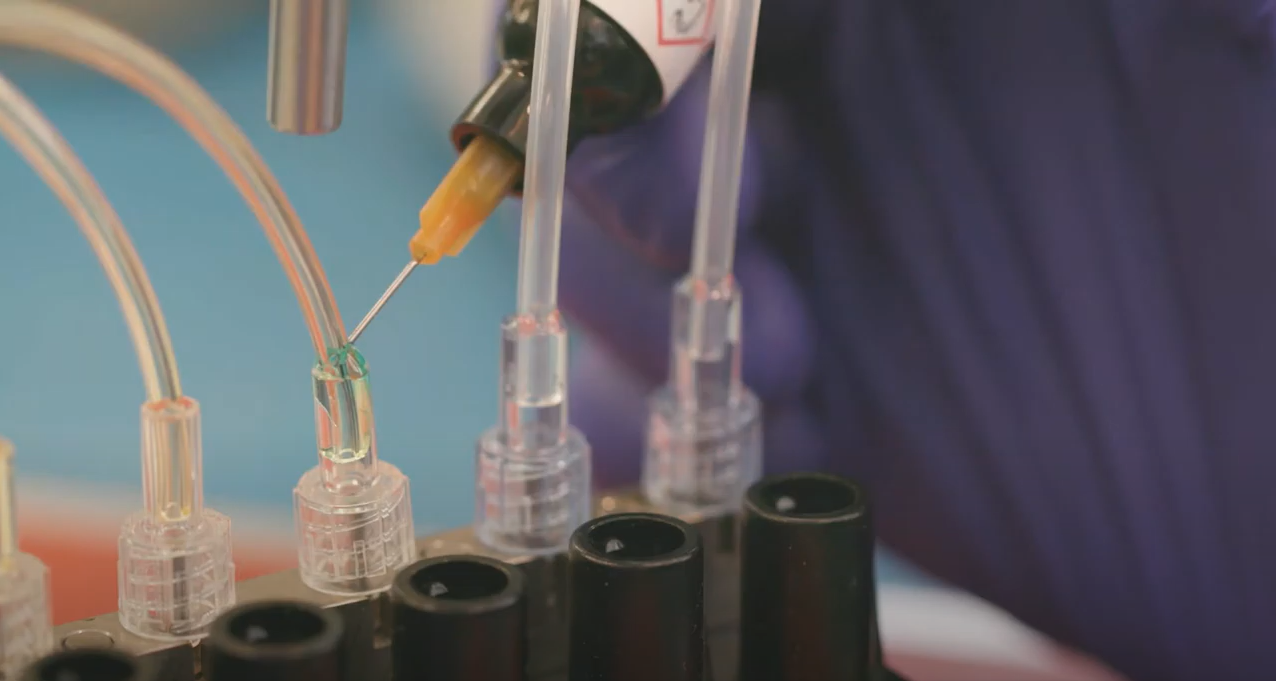
Assembling Medical Devices
Over the past decade, medical devices have become more intricate, leading manufacturers to focus on quality to eliminate production failures, defects, and field failures. When it comes to assembling your medical device, you want to be able to achieve consistent quality results, as lives may be at risk. From mechanical to chemical bonding, several assembly techniques are available for joining plastic parts.
Here are the best 4 medical device assembly techniques:
Mechanical fasteners such as bolted assemblies and rivets require a hole – a point of weakness - to be made in the substrate. Fasteners are not suitable for small and delicate assemblies. They can only be used for larger, heavier-weight plastic assemblies that can handle the strain and high stress occurring at the insertion site.
Ultrasonic welding, also known as fusion bonding, requires heating each plastic substrate, then holding the melted edges together by applying pressure until the two parts meld into one as the plastic cools. This process is functional, but gaps remain in the assembly due to bond-gap variances.
Solvent welding is a similar process. It involves coating plastic parts with a solvent and pressing them together until the solvent evaporates and the parts are fused. However, this process comes with a high risk of stress cracking the plastic substrate. In addition, solvent emissions can be very hazardous.
Adhesives can also bond plastic parts together while offering distinct advantages over other bonding processes. Although they require setting and curing time, adhesive bonding is more efficient and easier than alternatives. To find out more check this infographic.
Need help deciding which technique is best for your application? Our application engineers are happy to provide you with a free consultation.
_________________________________________________________
Enjoying This Content? Let’s Stay Connected.
If you’re finding value in our insights, why not get more of it—delivered right to your inbox? Subscribe to receive the latest technical articles, white papers, product news, and expert tips.